| CaseStudyForm | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Extended Health Clinic | ||||||||||||
| DateSubmitted | 25 Sep 2017 | ||||||||||||
| CaseStudyType | TeachingCaseStudy | ||||||||||||
| OperationsResearchTopics | SimulationModelling | ||||||||||||
| ApplicationAreas | Healthcare | ||||||||||||
| ProblemDescription |
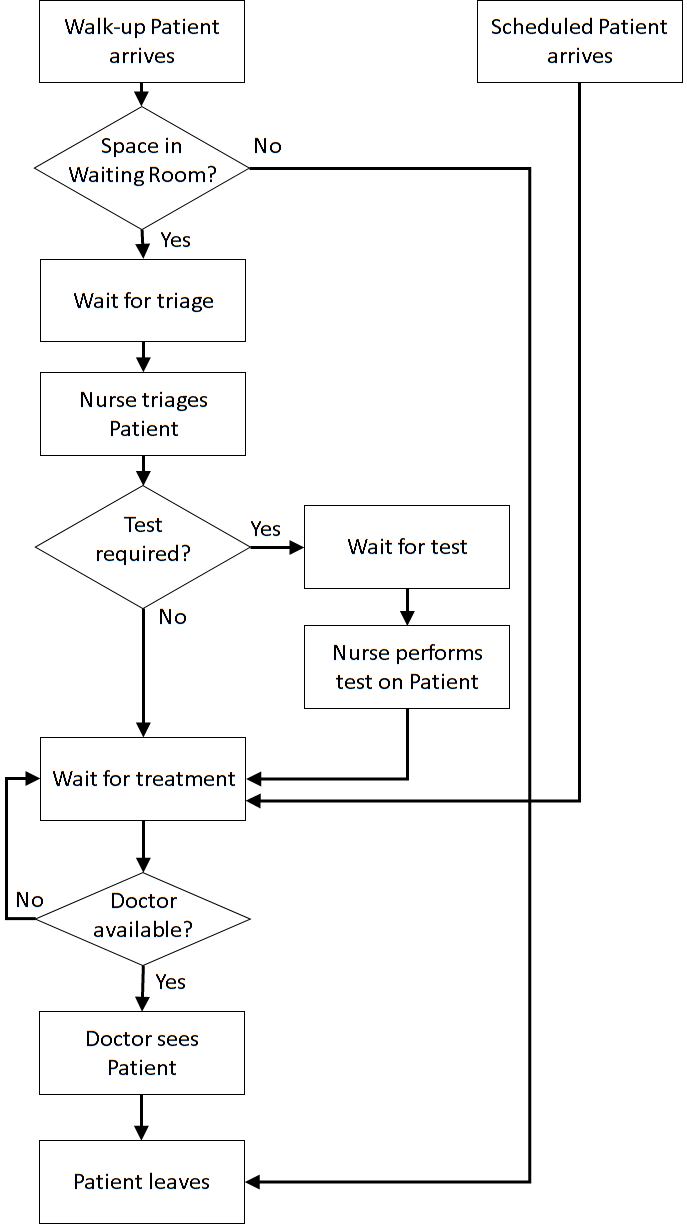
This case study extends the Simple Health Clinic – Scheduled Appointments model. The extensions are:
| ||||||||||||
| ProblemFormulation |
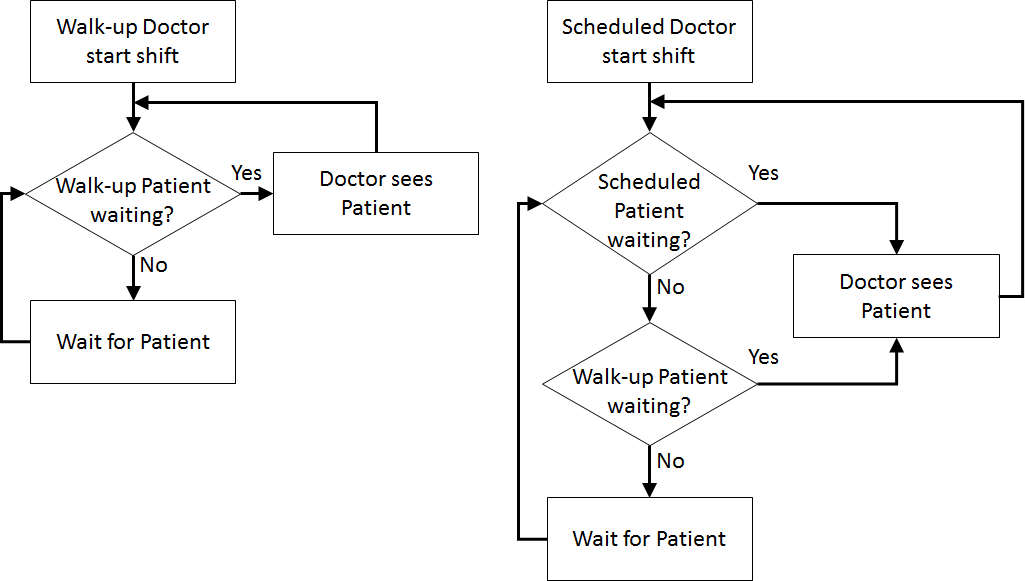
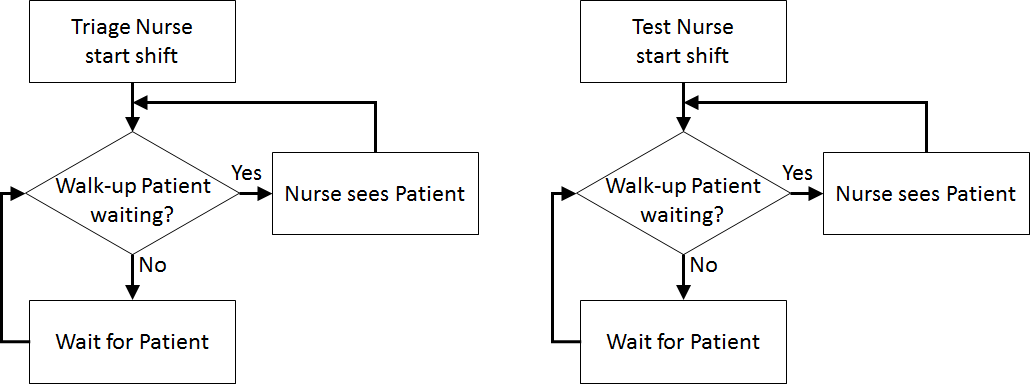
In order to formulate a simulation model we specify the following components:
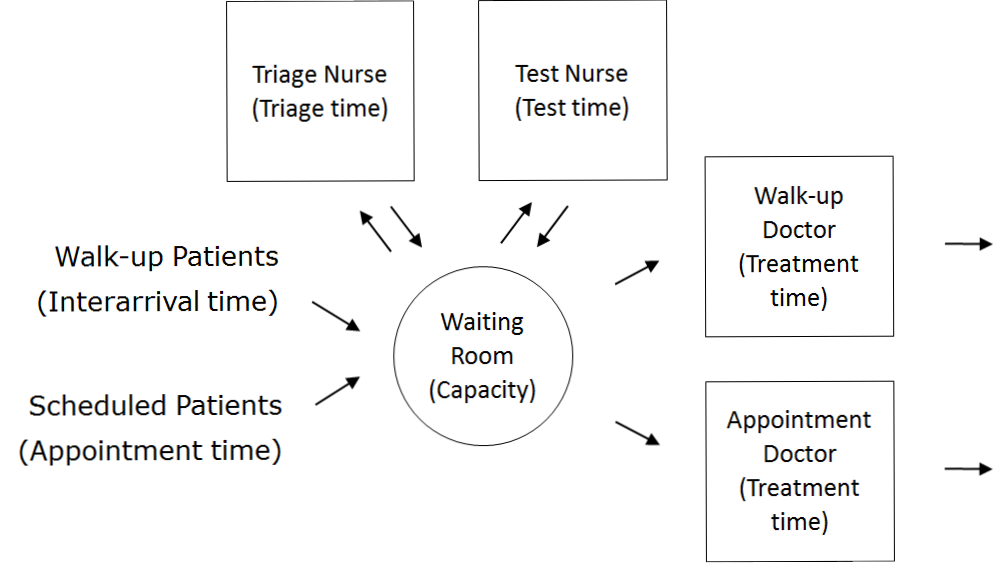
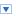
 Once the content has been established (note this is usually an iterative process) we can identify the inputs and outputs: appointment times, interarrival times, triage times, test times, treatment times, waiting times for triage, testing, and treatment (i.e., Patient arrives to Nurse triages Patient, Nurse triages Patient to Nurse performs test on Patient, Nurse performs test on Patient to Doctor sees Patient, Nurse triages Patient to Doctor sees Patient, Patient arrives to Doctor sees Patient), total clinic time (Patient arrives to Outside), number in waiting room.
Assumptions are used to define stochasticity (e.g., Exponential interarrivals, Triangular treatment times) and the simplifications keep the system simple (e.g., single doctors and nurses on all day for triage, testing, and treatment, no registration, no prioritisation).
Once the content has been established (note this is usually an iterative process) we can identify the inputs and outputs: appointment times, interarrival times, triage times, test times, treatment times, waiting times for triage, testing, and treatment (i.e., Patient arrives to Nurse triages Patient, Nurse triages Patient to Nurse performs test on Patient, Nurse performs test on Patient to Doctor sees Patient, Nurse triages Patient to Doctor sees Patient, Patient arrives to Doctor sees Patient), total clinic time (Patient arrives to Outside), number in waiting room.
Assumptions are used to define stochasticity (e.g., Exponential interarrivals, Triangular treatment times) and the simplifications keep the system simple (e.g., single doctors and nurses on all day for triage, testing, and treatment, no registration, no prioritisation).
| ||||||||||||
| ComputationalModel |
Start with the Simple Health Clinic – Scheduled Appointments JaamSim model.
 Select the PatientEntity and add a Test attribute to the AttributeDefinitionList by adding { Test 0} to the list.
Select the PatientEntity and add a Test attribute to the AttributeDefinitionList by adding { Test 0} to the list.
 Now add a distribution that determines if a Walk-Up patient needs a test or not. Add a DiscreteDistribution object from Model Palette > Probability Distributions. Name it TestDistribution and edit it so that 30% of Walk-Up patients require tests.
Now add a distribution that determines if a Walk-Up patient needs a test or not. Add a DiscreteDistribution object from Model Palette > Probability Distributions. Name it TestDistribution and edit it so that 30% of Walk-Up patients require tests.
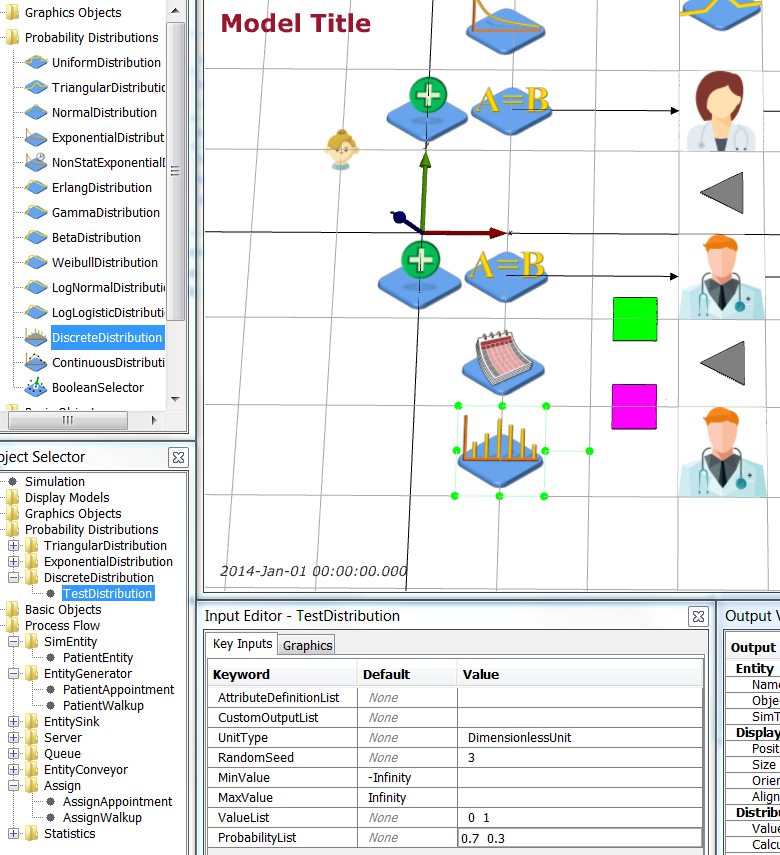 | Object | Graphics | Key Inputs |
| TestDistribution | Position = 1 -2.5 0.0 m | UnitType = DimensionlessUnit, ValueList = 0 1, ProbabilityList = 0.7 0.3 |
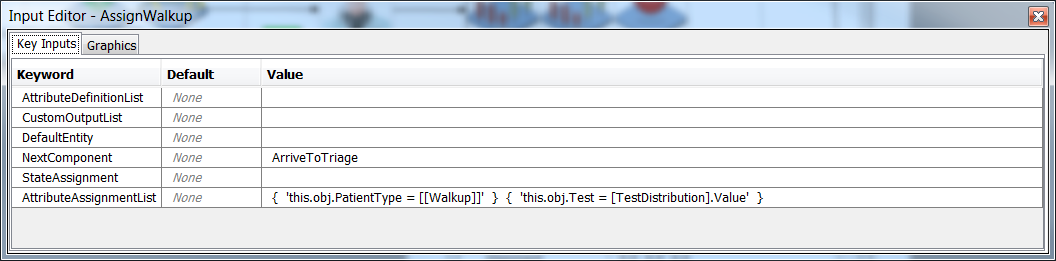
Now select the AssignWalkup object and add {
| Object | Graphics | Key Inputs |
| TestDistribution | Position = 1 -2.5 0.0 m | UnitType = DimensionlessUnit, ValueList = 0 1, ProbabilityList = 0.7 0.3 |
Now select the AssignWalkup object and add { 'this.obj.Test = [TestDistribution].Value' } to AttributeAssignmentList.
 Save your simulation.
Next, create two new servers (Process Flow > Server), one for triage and one for testing. Name then NurseTriage and NurseTest respectively and give them the nurse.png (icon made by Freepik from www.flaticon.com
Save your simulation.
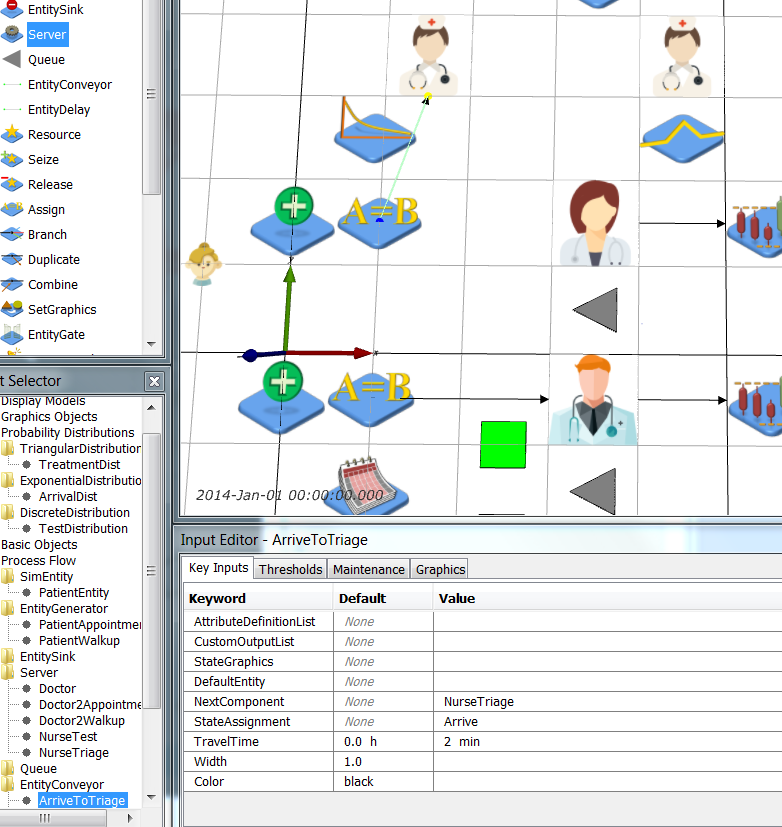
Next, create two new servers (Process Flow > Server), one for triage and one for testing. Name then NurseTriage and NurseTest respectively and give them the nurse.png (icon made by Freepik from www.flaticon.com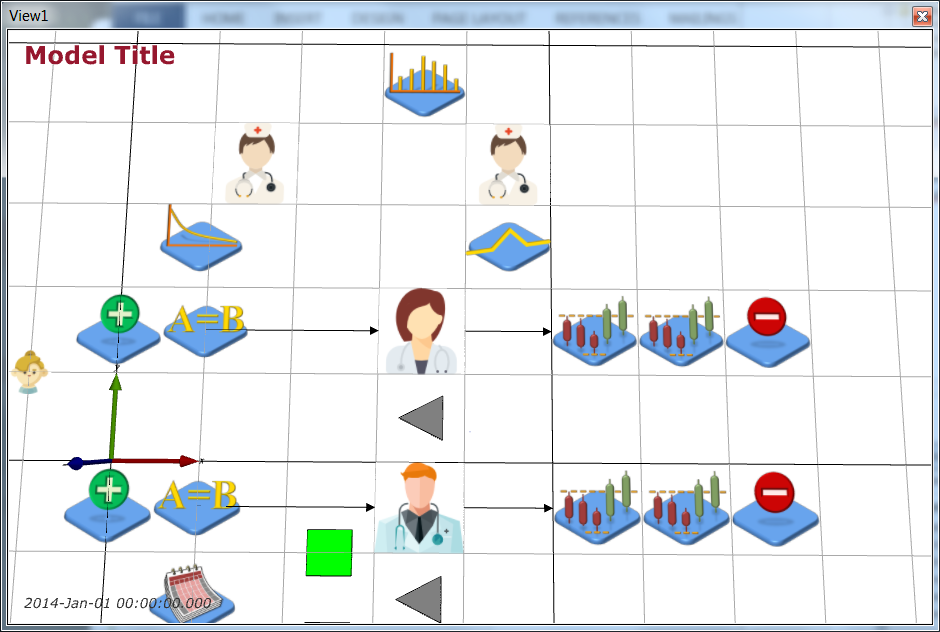 Rename the ArriveToTreat EntityConveyor to be ArriveToTriage and change NextComponent to be NurseTriage. You can redirect the EntityConveyor by clicking on it, then Ctrl-clicking on its end point and dragging it to where you want it to be. Redirect ArriveToTriage as shown below:
Rename the ArriveToTreat EntityConveyor to be ArriveToTriage and change NextComponent to be NurseTriage. You can redirect the EntityConveyor by clicking on it, then Ctrl-clicking on its end point and dragging it to where you want it to be. Redirect ArriveToTriage as shown below:
 Next, we need to add the branching for the potential test. Add a Branch object (Model Palette > Process Flow > Branch) and name it TestBranch. Now add 3 more EntityConveyors: TriageToDoctor, TriageToTest, TestToDoctor. TestBranch and the 3 conveyors are shown below (TriageToTest going horizontal left to right, TriageToDoctor diagonally down left, TestToDoctor diagonally down left).
Next, we need to add the branching for the potential test. Add a Branch object (Model Palette > Process Flow > Branch) and name it TestBranch. Now add 3 more EntityConveyors: TriageToDoctor, TriageToTest, TestToDoctor. TestBranch and the 3 conveyors are shown below (TriageToTest going horizontal left to right, TriageToDoctor diagonally down left, TestToDoctor diagonally down left).
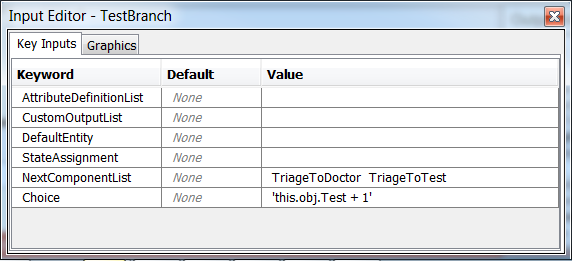
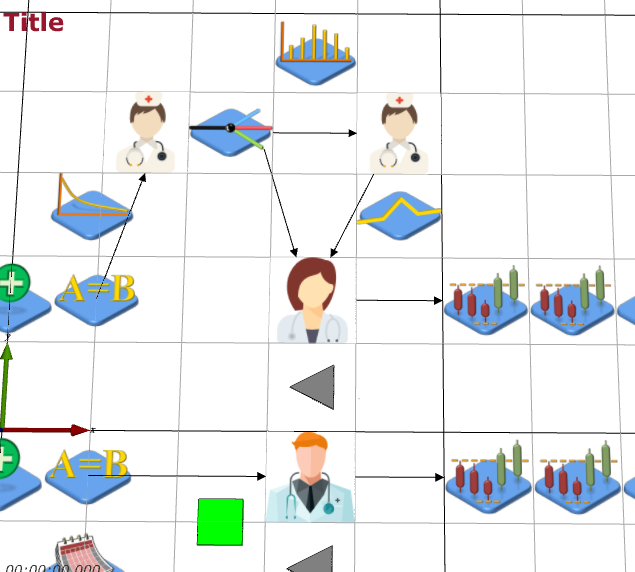 Next, make sure that the flow of the patients through the triage and test conveyors and servers is set correctly. The TestBranch object uses the value of the entities' Test attribute with 1 added to it to transform it from a {0, 1} value to a {1, 2} value (JaamSim starts lists at 1 not 0), so a patient that doesn't need a test (Test = 0) goes to the first component in the list, i.e., TriageToDoctor conveyor.
Next, make sure that the flow of the patients through the triage and test conveyors and servers is set correctly. The TestBranch object uses the value of the entities' Test attribute with 1 added to it to transform it from a {0, 1} value to a {1, 2} value (JaamSim starts lists at 1 not 0), so a patient that doesn't need a test (Test = 0) goes to the first component in the list, i.e., TriageToDoctor conveyor.
 | Object | Key Inputs |
| TestDistribution | UnitType = DimensionlessUnit, ValueList = 0 1, ProbabilityList = 0.7 0.3 |
| Object | Key Inputs |
| TestDistribution | UnitType = DimensionlessUnit, ValueList = 0 1, ProbabilityList = 0.7 0.3 |
| ||||||||||||
| Results | The results... | ||||||||||||
| Conclusions | In conclusion... | ||||||||||||
| ExtraForExperts | |||||||||||||
| StudentTasks | |||||||||||||
Topic revision: r4 - 2017-09-28 - MichaelOSullivan
Ideas, requests, problems regarding TWiki? Send feedback