| CaseStudyForm | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Extended Health Clinic | ||||||||||||
| DateSubmitted | 25 Sep 2017 | ||||||||||||
| CaseStudyType | TeachingCaseStudy | ||||||||||||
| OperationsResearchTopics | SimulationModelling | ||||||||||||
| ApplicationAreas | Healthcare | ||||||||||||
| ProblemDescription |
This case study extends the Simple Health Clinic – Scheduled Appointments model. The extensions are:
| ||||||||||||
| ProblemFormulation |
In order to formulate a simulation model we specify the following components:
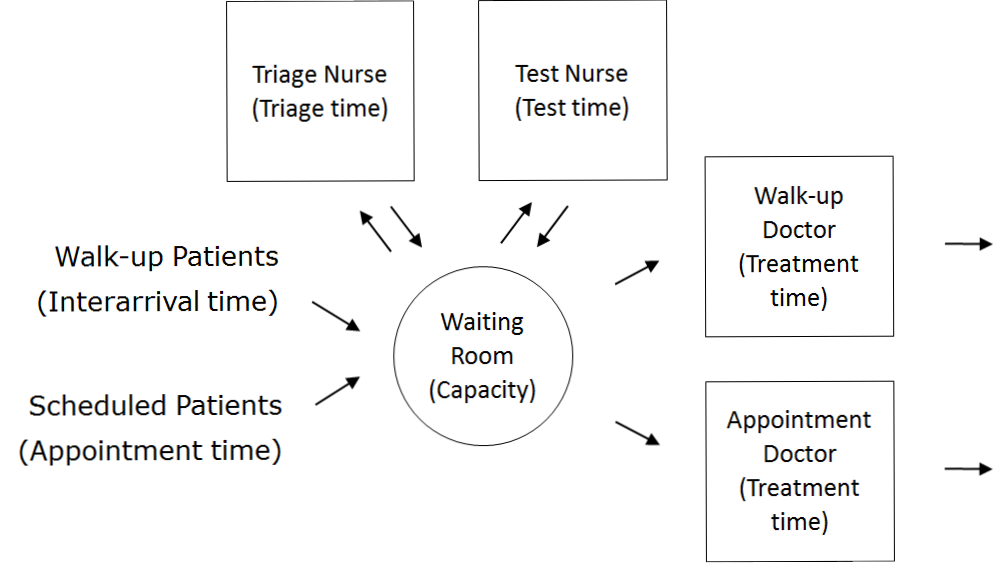
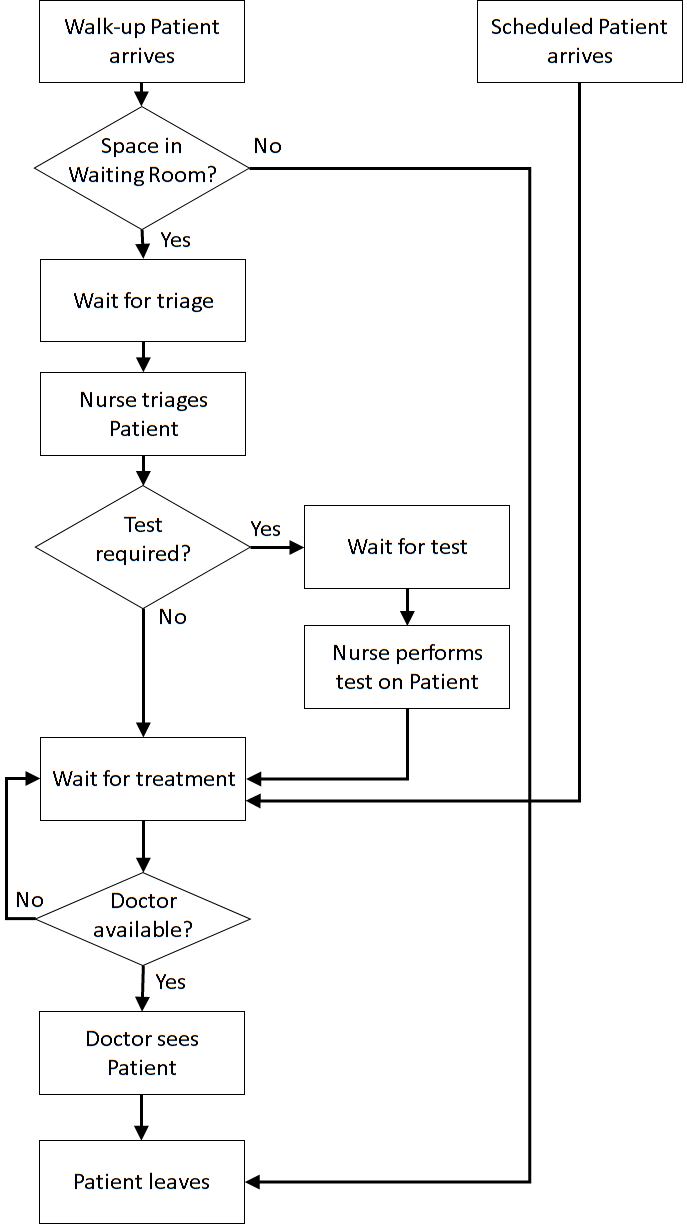
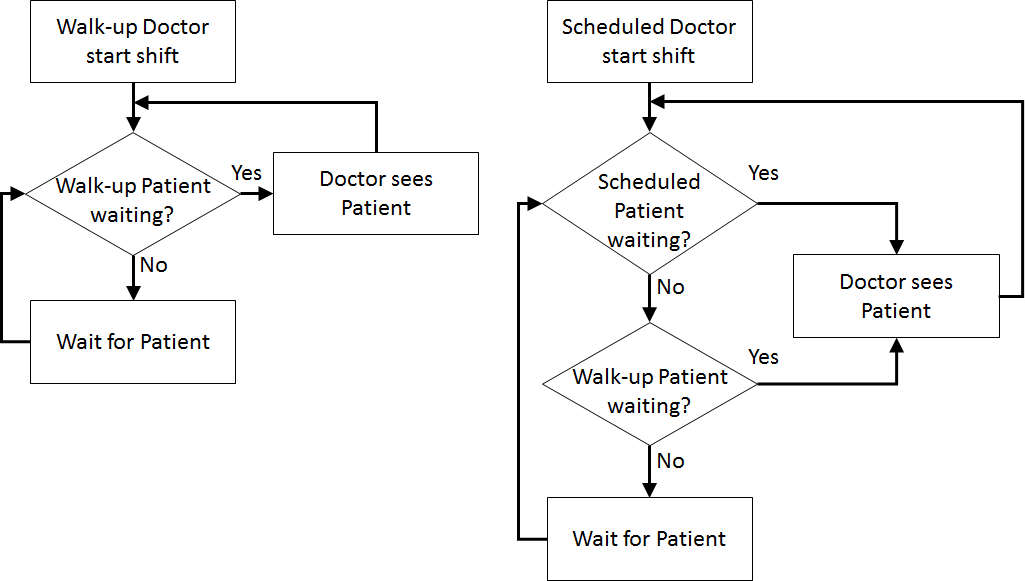
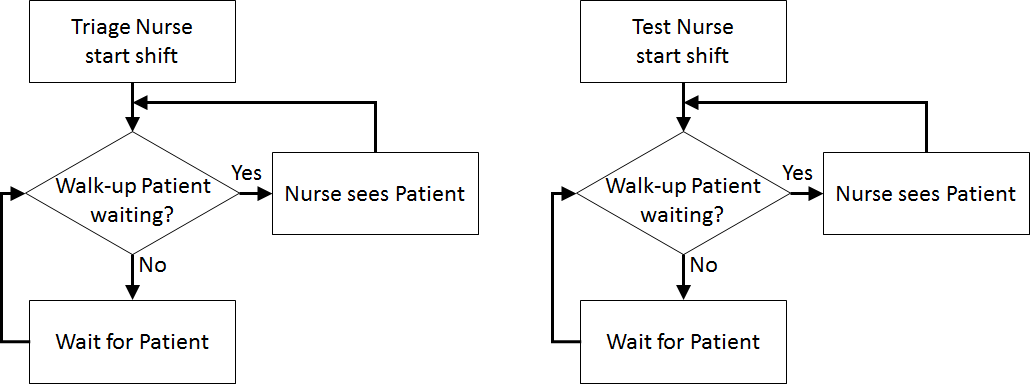
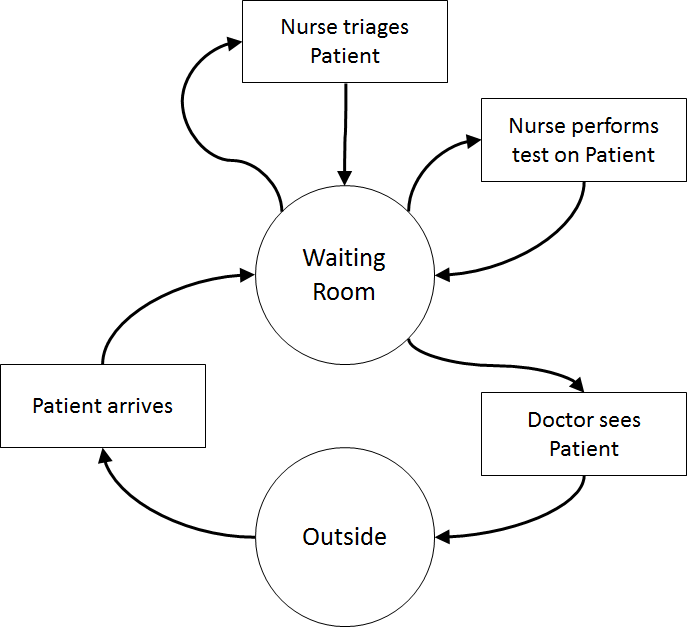 Once the content has been established (note this is usually an iterative process) we can identify the inputs and outputs: appointment times, interarrival times, triage times, test times, treatment times, waiting times for triage, testing, and treatment (i.e., Patient arrives to Nurse triages Patient, Nurse triages Patient to Nurse performs test on Patient, Nurse performs test on Patient to Doctor sees Patient, Nurse triages Patient to Doctor sees Patient, Patient arrives to Doctor sees Patient), total clinic time (Patient arrives to Outside), number in waiting room.
Assumptions are used to define stochasticity (e.g., Exponential interarrivals, Triangular treatment times) and the simplifications keep the system simple (e.g., single doctors and nurses on all day for triage, testing, and treatment, no registration, no prioritisation).
Once the content has been established (note this is usually an iterative process) we can identify the inputs and outputs: appointment times, interarrival times, triage times, test times, treatment times, waiting times for triage, testing, and treatment (i.e., Patient arrives to Nurse triages Patient, Nurse triages Patient to Nurse performs test on Patient, Nurse performs test on Patient to Doctor sees Patient, Nurse triages Patient to Doctor sees Patient, Patient arrives to Doctor sees Patient), total clinic time (Patient arrives to Outside), number in waiting room.
Assumptions are used to define stochasticity (e.g., Exponential interarrivals, Triangular treatment times) and the simplifications keep the system simple (e.g., single doctors and nurses on all day for triage, testing, and treatment, no registration, no prioritisation).
| ||||||||||||
| ComputationalModel |
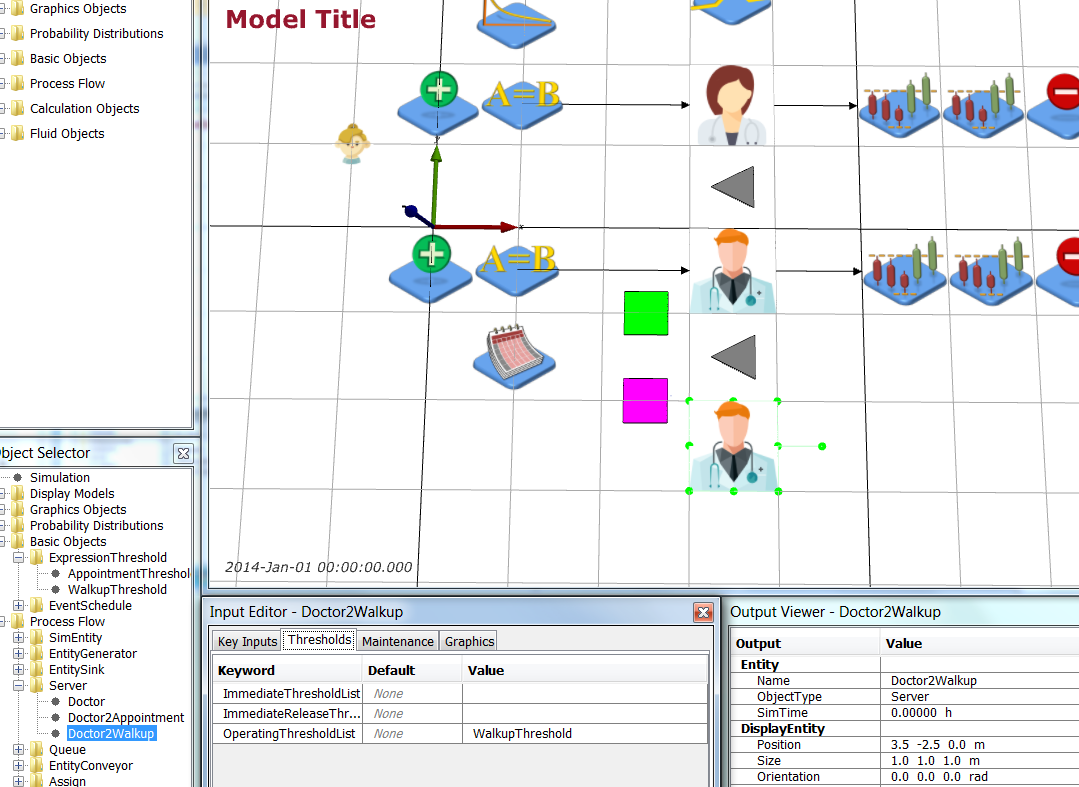
Start with the Simple Health Clinic – Scheduled Appointments JaamSim model.
| ||||||||||||
| Results | The results... | ||||||||||||
| Conclusions | In conclusion... | ||||||||||||
| ExtraForExperts | |||||||||||||
| StudentTasks | |||||||||||||
Topic revision: r1 - 2017-09-25 - MichaelOSullivan
Ideas, requests, problems regarding TWiki? Send feedback