
Difference: DataNetworkFlows (1 vs. 9)
Revision 92009-09-07 - TWikiAdminUser
| Line: 1 to 1 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
<-- Under Construction --> | ||||||||||
| Line: 86 to 86 | ||||||||||
| ||||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||||
| < < | |*FORM FIELD ProblemDescription*|ProblemDescription|*THE DATA FLOW PROBLEM*
Adapted from a real-world problem
Many large companies are starting to centralise their data storage. Centralised data storage allows for increased efficiency of data storage resources, security of the data and reliability of the storage system. Storage Area Networks ("SANs") are a popular way to provide centralised storage. SANs connect servers and/or client machines (known as hosts) to the centralised data storage devices using a network of links (ethernet, fibre channel and/or SCSI cables), hubs and switches.
The problem facing network/storage engineers is how to build a cost-efficient, reliable SAN.
To answer this question, we must first consider the different components of this example SAN:
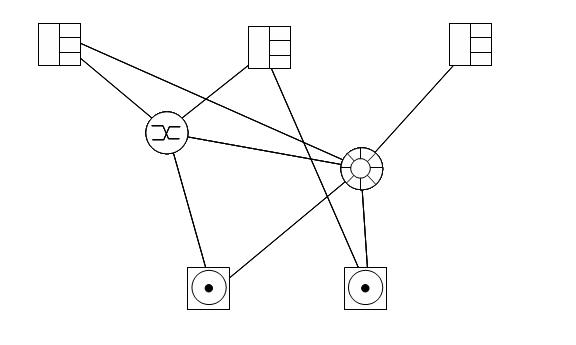 HOSTS
The hosts are web servers, application servers, client machines, etc. They have a number of port slots for network interface cards (NICs). Each slot has a specified port bandwidth capacity and a port cost (the cost of the NIC to put in the port slot).
HOSTS
The hosts are web servers, application servers, client machines, etc. They have a number of port slots for network interface cards (NICs). Each slot has a specified port bandwidth capacity and a port cost (the cost of the NIC to put in the port slot).
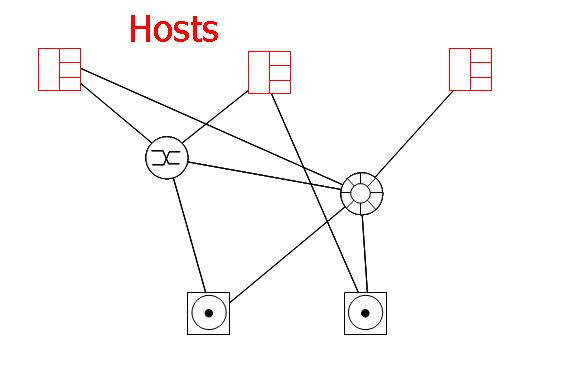 DEVICES
The (storage) devices are disks, disk arrays, tape drives, etc. They have the same attributes as hosts, namely a number of port slots, port bandwidth capacity and port cost.
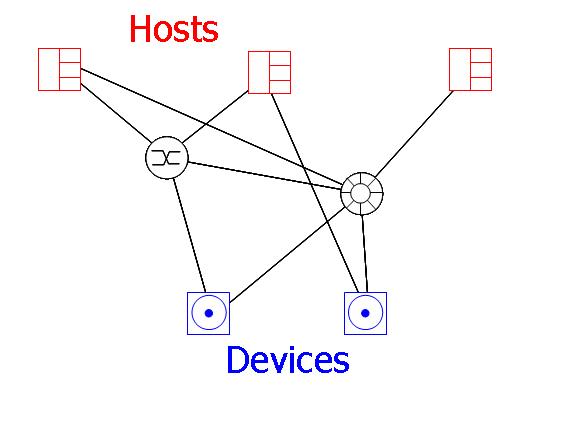
DEVICES
The (storage) devices are disks, disk arrays, tape drives, etc. They have the same attributes as hosts, namely a number of port slots, port bandwidth capacity and port cost.
 HUBS
Hubs are one type of aggregation point in a network. They can connect several other components (hosts, devices, switches). However, hubs are essentially loops and any flow going into a hub must visit all the links and ports connected to the hub before leaving to its destination.
HUBS
Hubs are one type of aggregation point in a network. They can connect several other components (hosts, devices, switches). However, hubs are essentially loops and any flow going into a hub must visit all the links and ports connected to the hub before leaving to its destination.
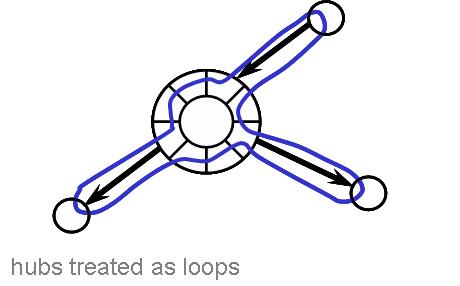 This means that the overall hub bandwidth is restricted by the connections made to the hub (that is, the overall hub bandwidth is less than or equal to the minimum of the link bandwidths connected to it). Hubs have a number of port slots, a cost and an overall bandwidth capacity. Hubs come with their port slots preconfigured, i.e., no NIC cards need to be purchased, and the port bandwidth capacity is the same as the overall capacity (for the reason specified earlier).
This means that the overall hub bandwidth is restricted by the connections made to the hub (that is, the overall hub bandwidth is less than or equal to the minimum of the link bandwidths connected to it). Hubs have a number of port slots, a cost and an overall bandwidth capacity. Hubs come with their port slots preconfigured, i.e., no NIC cards need to be purchased, and the port bandwidth capacity is the same as the overall capacity (for the reason specified earlier).
 SWITCHES
Switches are the other type of aggregation point in a network. Unlike hubs, switches route data intelligently, so each port operates inependently. Switches have a number of port slots without NICs, so there is also a port cost for purchasing a NIC. Since the ports operate independently, their port slots have a port bandwidth capacity. There is also the cost of the entire switch to take into account.
SWITCHES
Switches are the other type of aggregation point in a network. Unlike hubs, switches route data intelligently, so each port operates inependently. Switches have a number of port slots without NICs, so there is also a port cost for purchasing a NIC. Since the ports operate independently, their port slots have a port bandwidth capacity. There is also the cost of the entire switch to take into account.
 LINKS
Finally, links are simply cables that connect one port (or NIC in a port slot) to another. They are typically ethernet, fibre channel or SCSI. Links have a cost and a bandwidth capacity.
LINKS
Finally, links are simply cables that connect one port (or NIC in a port slot) to another. They are typically ethernet, fibre channel or SCSI. Links have a cost and a bandwidth capacity.
 MAXIMISING THROUGHPUT
A storage networking consultant has been provided with the following network diagram, with the bandwidth capacities shown. This network already exists, so all costs are zero.
MAXIMISING THROUGHPUT
A storage networking consultant has been provided with the following network diagram, with the bandwidth capacities shown. This network already exists, so all costs are zero.
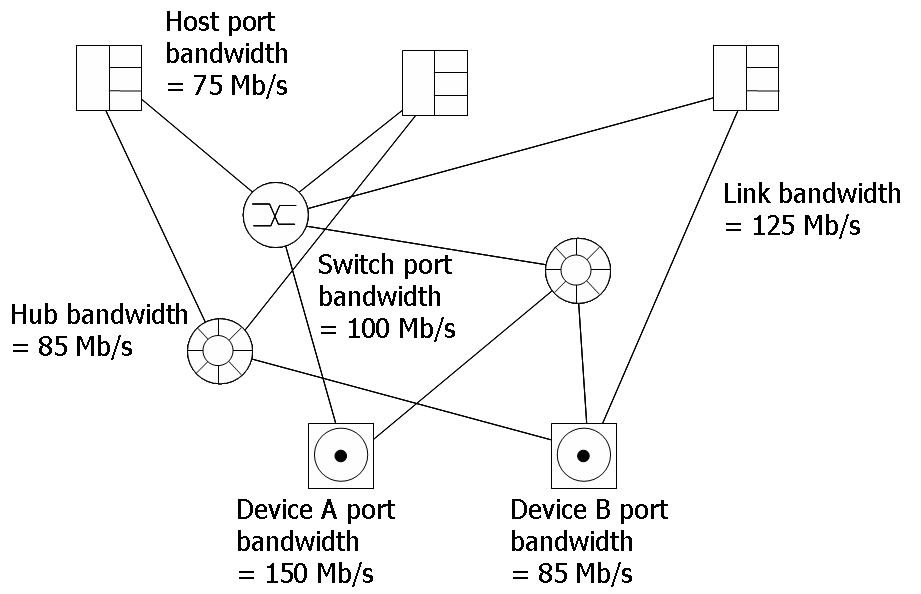 His client wants to send 110 MB/s of data from each host to the devices. Where should they send the data?
The cost of a link reduces as its bandwidth capacity decreases. What is the lowest bandwidth capacity for the links in the network that will still support the 110 MB/s flow from the hosts?
|
His client wants to send 110 MB/s of data from each host to the devices. Where should they send the data?
The cost of a link reduces as its bandwidth capacity decreases. What is the lowest bandwidth capacity for the links in the network that will still support the 110 MB/s flow from the hosts?
| | |||||||||
| > > | |*FORM FIELD ProblemDescription*|ProblemDescription|*THE DATA FLOW PROBLEM*
Adapted from a real-world problem
Many large companies are starting to centralise their data storage. Centralised data storage allows for increased efficiency of data storage resources, security of the data and reliability of the storage system. Storage Area Networks ("SANs") are a popular way to provide centralised storage. SANs connect servers and/or client machines (known as hosts) to the centralised data storage devices using a network of links (ethernet, fibre channel and/or SCSI cables), hubs and switches.
The problem facing network/storage engineers is how to build a cost-efficient, reliable SAN.
To answer this question, we must first consider the different components of this example SAN:
 HOSTS
The hosts are web servers, application servers, client machines, etc. They have a number of port slots for network interface cards (NICs). Each slot has a specified port bandwidth capacity and a port cost (the cost of the NIC to put in the port slot).
HOSTS
The hosts are web servers, application servers, client machines, etc. They have a number of port slots for network interface cards (NICs). Each slot has a specified port bandwidth capacity and a port cost (the cost of the NIC to put in the port slot).
 DEVICES
The (storage) devices are disks, disk arrays, tape drives, etc. They have the same attributes as hosts, namely a number of port slots, port bandwidth capacity and port cost.
DEVICES
The (storage) devices are disks, disk arrays, tape drives, etc. They have the same attributes as hosts, namely a number of port slots, port bandwidth capacity and port cost.
 HUBS
Hubs are one type of aggregation point in a network. They can connect several other components (hosts, devices, switches). However, hubs are essentially loops and any flow going into a hub must visit all the links and ports connected to the hub before leaving to its destination.
HUBS
Hubs are one type of aggregation point in a network. They can connect several other components (hosts, devices, switches). However, hubs are essentially loops and any flow going into a hub must visit all the links and ports connected to the hub before leaving to its destination.
 This means that the overall hub bandwidth is restricted by the connections made to the hub (that is, the overall hub bandwidth is less than or equal to the minimum of the link bandwidths connected to it). Hubs have a number of port slots, a cost and an overall bandwidth capacity. Hubs come with their port slots preconfigured, i.e., no NIC cards need to be purchased, and the port bandwidth capacity is the same as the overall capacity (for the reason specified earlier).
This means that the overall hub bandwidth is restricted by the connections made to the hub (that is, the overall hub bandwidth is less than or equal to the minimum of the link bandwidths connected to it). Hubs have a number of port slots, a cost and an overall bandwidth capacity. Hubs come with their port slots preconfigured, i.e., no NIC cards need to be purchased, and the port bandwidth capacity is the same as the overall capacity (for the reason specified earlier).
 SWITCHES
Switches are the other type of aggregation point in a network. Unlike hubs, switches route data intelligently, so each port operates independently. Switches have a number of port slots without NICs, so there is also a port cost for purchasing a NIC. Since the ports operate independently, their port slots have a port bandwidth capacity. There is also the cost of the entire switch to take into account.
SWITCHES
Switches are the other type of aggregation point in a network. Unlike hubs, switches route data intelligently, so each port operates independently. Switches have a number of port slots without NICs, so there is also a port cost for purchasing a NIC. Since the ports operate independently, their port slots have a port bandwidth capacity. There is also the cost of the entire switch to take into account.
 LINKS
Finally, links are simply cables that connect one port (or NIC in a port slot) to another. They are typically ethernet, fibre channel or SCSI. Links have a cost and a bandwidth capacity.
LINKS
Finally, links are simply cables that connect one port (or NIC in a port slot) to another. They are typically ethernet, fibre channel or SCSI. Links have a cost and a bandwidth capacity.
 MAXIMISING THROUGHPUT
A storage networking consultant has been provided with the following network diagram, with the bandwidth capacities shown. This network already exists, so all costs are zero.
MAXIMISING THROUGHPUT
A storage networking consultant has been provided with the following network diagram, with the bandwidth capacities shown. This network already exists, so all costs are zero.
 His client wants to send 110 MB/s of data from each host to the devices. Where should they send the data?
The cost of a link reduces as its bandwidth capacity decreases. What is the lowest bandwidth capacity for the links in the network that will still support the 110 MB/s flow from the hosts?
|
His client wants to send 110 MB/s of data from each host to the devices. Where should they send the data?
The cost of a link reduces as its bandwidth capacity decreases. What is the lowest bandwidth capacity for the links in the network that will still support the 110 MB/s flow from the hosts?
| | |||||||||
| ||||||||||
Revision 82009-06-29 - TWikiAdminUser
| Line: 1 to 1 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
<-- Under Construction --> | ||||||||||
| Line: 92 to 92 | ||||||||||
| ||||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||||
| < < | |*FORM FIELD StudentTasks*|StudentTasks|*STUDENT TASKS* ??? Mike to check this form???
The consultant has written some AMPL files to solve his problem. He has completed
EXTRA FOR EXPERTS' TASKS
san.mod and san.dat, but could not complete his script file san.run. Note You should be able to cut-and-paste san.mod, san.dat and (the incomplete) san.run.
??? See san.mod, san.run, san.dat attachments ???
san.run file. Your management summary.
1. The client now wants to know what is the maximum total bandwidth the network will support. Modify |
san.run to answer this question. Write a management summary for your solution.
What to hand in Your modified san.run file. Your new management summary.
| |||||||||
| > > | |*FORM FIELD StudentTasks*|StudentTasks|*STUDENT TASKS*
The consultant has written some AMPL files to solve his problem. He has completed
EXTRA FOR EXPERTS' TASKS
san.mod and san.dat, but could not complete his script file san.run (his incomplete version is attached, san_incomplete.run)
* san.mod
* san.dat
* san_incomplete.run
1. Complete the script file san.run to find the data flows and discover the lowest link capacity that supports the client's bandwidth. Write a management summary for your solutions.
1. The client now wants to know what is the maximum total bandwidth the network will support. Modify |san.run to answer this question. Write a management summary for your solution.
What to hand in Your modified san.run file. Your new management summary.
| |||||||||
| ||||||||||
| Line: 104 to 101 | ||||||||||
| ||||||||||
| Added: | ||||||||||
| > > |
| |||||||||
Revision 72008-04-02 - MichaelOSullivan
| Line: 1 to 1 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
<-- Under Construction --> | ||||||||
| Line: 40 to 40 | ||||||||
| Return to top | ||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||
| < < | Computational Model | |||||||
| > > | Computational Model | |||||||
| The computational model... | ||||||||
| Line: 48 to 48 | ||||||||
| Return to top | ||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||
| < < | Results | |||||||
| > > | Results | |||||||
| The results... | ||||||||
| Line: 56 to 56 | ||||||||
| Return to top | ||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||
| < < | Conclusions | |||||||
| > > | Conclusions | |||||||
| In conclusion... | ||||||||
Revision 62008-03-01 - TWikiAdminUser
| Line: 1 to 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
<-- Under Construction --> | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Deleted: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| < < | <-- Ready to Review --> | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Revision 52008-03-01 - TWikiAdminUser
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||