| |
| META TOPICPARENT |
name="ArenaGuide" |
Editing Assign Modules |
| |
Variables may be assigned a new value by setting the Type to be Variable, the Variable Name to the name of the variable to assign and New Value to the new value of the variable. |
|
<
< | One dimensional variables may be useful when dealing with arrays, e.g. using different variable values for each day of the week. One dimensional variables may be assigned a new value by setting the Type to be Variable Array (1D), choosing the required Ro of the array and setting the New Value. Note that the variable array must be set up (see Editing Variables) with the correct number of rows for the assignment to work correctly. |
>
> | One dimensional variables may be useful when dealing with arrays, e.g. using different variable values for each day of the week. One dimensional variables may be assigned a new value by setting the Type to be Variable Array (1D), choosing the required Row of the array and setting the New Value. Note that the variable array must be set up (see Editing Variables) with the correct number of rows for the assignment to work correctly. |
| |
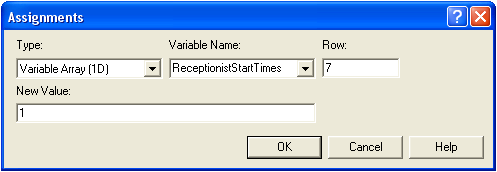
For example, assuming a variable array has been set up with initial values as shown. |
| |
 |
|
<
< | Note: Row 1 represents Monday, Row 2 represents Tuesday...etc |
>
> | NB : Row 1 represents Monday, Row 2 represents Tuesday...etc |
| | |
|
<
< | Two dimensional variables may also be useful. They are implemented identically to one dimensional variables (above) except that the user can define the number of rows and the number of columns. |
>
> | Two dimensional variables are useful when dealing with 2D arrays, e.g. using different variable values for different employees on different days of the week. They are implemented identically to one dimensional variables (above) except that the user can define the number of rows and the number of columns. |
| |
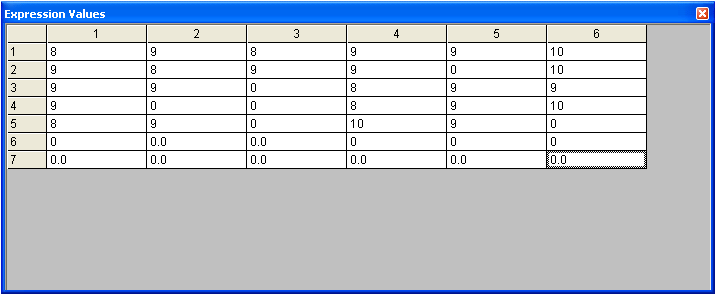
A good example of a 2D variable is assigning a roster for when several receptionists must start work each day. This example is shown below. |
|
<
< | Note: Row 1 represents Monday, Row 2 represents Tuesday...etc |
>
> | NB : Column 1 represents Receptionist 1 (e.g. Mary) , Column 2 represents Receptionist 2 (e.g. Jenny)...etc |
| | |
|
<
< | Note: Column 1 represents Receptionist 1 (e.g. Mary) , Column 2 represents Receptionist 2 (e.g. Jenny)...etc
Note: An entry of 0 on a weekday means that receptionist does not work on that day. |
>
> | NB: An entry of 0 on a weekday means that receptionist does not work on that day. |
| |
Attributes |
|
<
< | Entities can have Attributes assigned to them. There are also some special types of Attributes. Examples of Attributes and special types of Attributes are given below based on a medical centre situation. |
>
> | Entities can have Attributes assigned to them. |
| | |
|
<
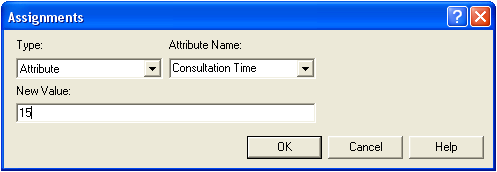
< | Each Attribute must be named and assigned a specific value. |
>
> | Each Attribute must be named and assigned a specific value. Attributes may be assigned by setting the Type to Attribute, defining a specific Attribute Name and setting the New Value. |
| |
 |
|
>
> | Entity Type |
| |
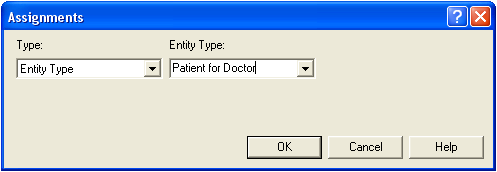
Entity.Type is a special kind of Attribute that refers to one of the specific types of entities defined in the model. |
|
>
> | The Entity.Type Attribute may be assigned by setting the Type to Entity Type and defining the Entity.Type. |
| |  |
|
>
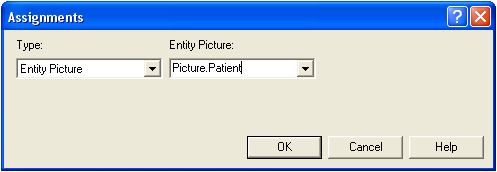
> | Entity Picture
Entity.Picture is a special kind of Attribute that stores the value of an entity's graphical picture to be used for animations within an Arena model.
The Entity.Picture Attribute may be assigned by setting the Type to Entity Picture and defining the Entity.Picture. |
| | |
|
<
< | Entity.Picture is a special kind of Attribute that stores the value of an entity's graphical picture to be used for animations within the Arena model. |
>
> | NB: A selection of pictures can be found in the Arena Libraries (See Arena Help for more details) |
| |
 |

